Vedas In Hindi Pdf
The purpose of this PDF file is to permit of 1) easy searching and 2) easy extracting. I wrote a special programme to generate this searchable and extractable PDF file. 1) Searching: The entire Rigveda text was converted to a clean 7-bit ASCII file for this PDF file, i.e. This file does not contain any diacritical characters. Pain vs naruto. The Vedas are classified into four volumes: the Rig-Veda, the Sama Veda, the Yajur Veda and the Atharva Veda, with the Rig Veda serving as the principal text. The four Vedas are collectively known as “Chathurveda, ” of which the first three Vedas--Rig Veda, Sama Veda, and Yajur Veda--agree with one another in form, language and content.
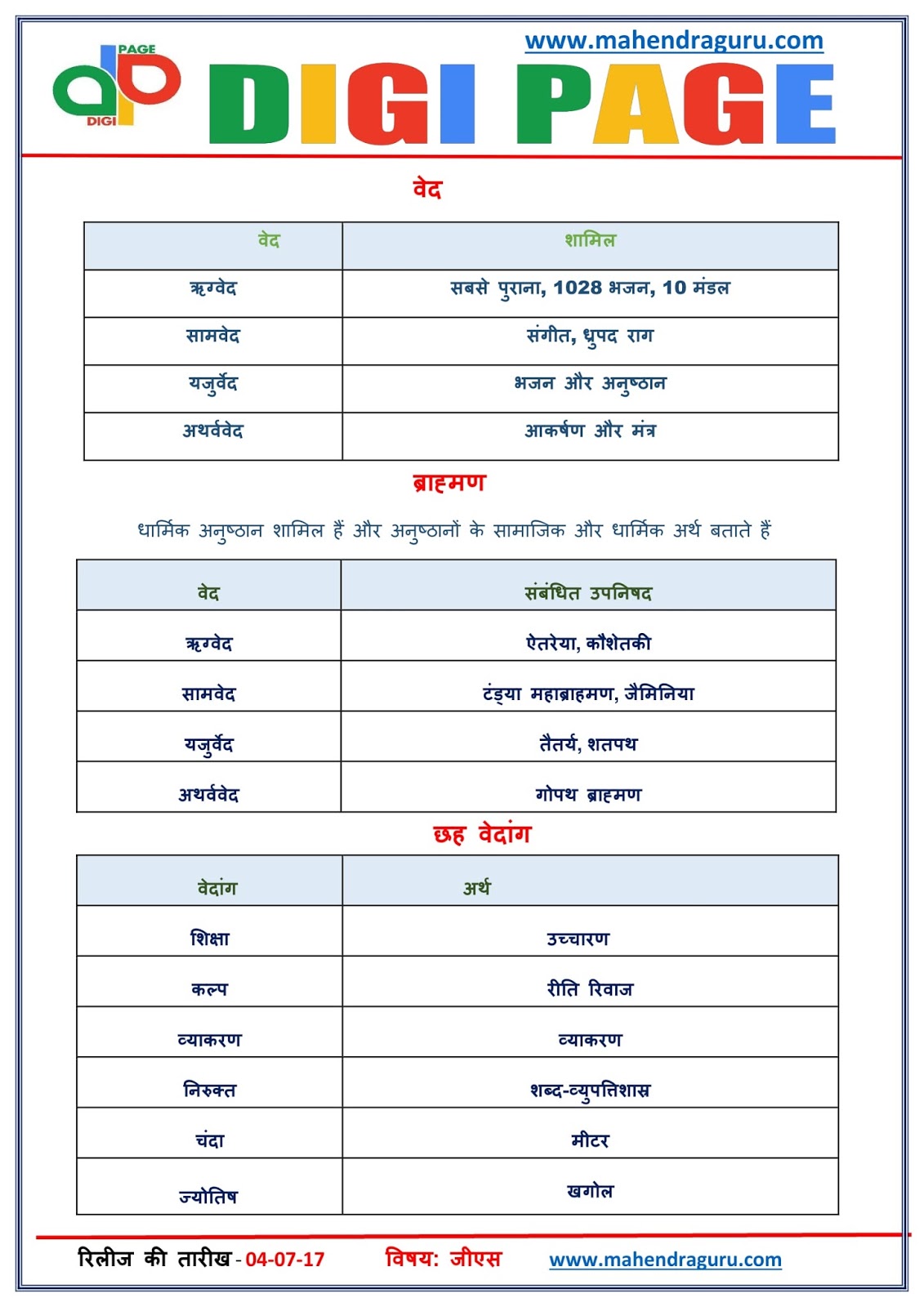
The Four Vedas In Pdf
See also: Rigvedic deities The Rigvedic hymns are dedicated to various deities, chief of whom are Indra, a heroic god praised for having slain his enemy Vrtra; Agni, the sacrificial fire; and Soma, the sacred potion or the plant it is made from. Kannada mp3 songs free download for mobile. Equally prominent gods are the Adityas or Asura gods Mitra–Varuna and Ushas (the dawn). Also invoked are Savitr, Vishnu, Rudra, Pushan, Brihaspati or Brahmanaspati, as well as deified natural phenomena such as Dyaus Pita (the shining sky, Father Heaven ), Prithivi (the earth, Mother Earth), Surya (the sun god), Vayu or Vata (the wind), Apas (the waters),Parjanya (the thunder and rain), Vac (the word), many rivers (notably the Sapta Sindhu, and the Sarasvati River). The Adityas, Vasus, Rudras, Sadhyas, Ashvins, Maruts, Rbhus, and theVishvadevas ('all-gods') as well as the 'thirty-three gods' are the groups of deities mentioned. The hymns mention various further minor gods, persons, phenomena and items, and contain fragmentary references to possible historical events, notably the struggle between the early Vedic people (known as Vedic Aryans, a subgroup of the Indo-Aryans) and their enemies, the Dasa or Dasyu and their mythical prototypes, the Paṇi (the Bactrian Parna). See also: Brahmana Of the Brahmanas that were handed down in the schools of the Bahvṛcas (i.e. 'possessed of many verses'), as the followers of the Rigveda are called, two have come down to us, namely those of the Aitareyins and the Kaushitakins.


Scientific Research In Vedas In Hindi
The Aitareya-brahmana [41] and the Kaushitaki- (or Sankhayana-) brahmana evidently have for their groundwork the same stock of traditional exegetic matter. They differ, however, considerably as regards both the arrangement of this matter and their stylistic handling of it, with the exception of the numerous legends common to both, in which the discrepancy is comparatively slight. There is also a certain amount of material peculiar to each of them.
Rig Veda In Hindi Pdf
The Kaushitaka is, upon the whole, far more concise in its style and more systematic in its arrangement features which would lead one to infer that it is probably the more modern work of the two. It consists of thirty chapters ( adhyaya); while the Aitareya has forty, divided into eight books (or pentads, pancaka), of five chapters each. The last ten adhyayas of the latter work are, however, clearly a later addition though they must have already formed part of it at the time of Pāṇini (ca. BC), if, as seems probable, one of his grammatical sutras, regulating the formation of the names of Brahmanas, consisting of thirty and forty adhyayas, refers to these two works. In this last portion occurs the well-known legend (also found in the Shankhayana-sutra, but not in the Kaushitaki-brahmana) of Shunahshepa, whom his father Ajigarta sells and offers to slay, the recital of which formed part of the inauguration of kings. While the Aitareya deals almost exclusively with the Soma sacrifice, the Kaushitaka, in its first six chapters, treats of the several kinds of haviryajna, or offerings of rice, milk, ghee, &c., whereupon follows the Soma sacrifice in this way, that chapters 7–10 contain the practical ceremonial and 11–30 the recitations ( shastra) of the hotar. Sayana, in the introduction to his commentary on the work, ascribes the Aitareya to the sage Mahidasa Aitareya (i.e.
Latest Posts
- Miss Pooja Mp3 Songs Download
- 3d Max 2017 Keygen
- Download Solidworks 2018
- Japanese Music Instrumental
- Free College Plagiarism Checker
- Josh Groban Bridges Cd Songs
- Windows 10 Pro Upgrade Download 64 Bit
- Fifa 18 Setup Exe
- Watch Prison Break Season 6
- Kuch Khaas Hai
- Microsoft Outlook Repair Software
- Ios Style Launcher For Android
- Tamil Kavithaigal In Tamil Language
- Xlstat Free Trial
- Overwatch Redeem Code Generator
- Mame Roms 197 Complete Set
- Basic English Grammar For Beginners
- Killer Bean Games
- Octopus Box V2.0.4 Crack
- Adobe Premiere Cs3 Free Download
- Flexisign Crack
- K3g Full Movie Online Free





